What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) & How It Works
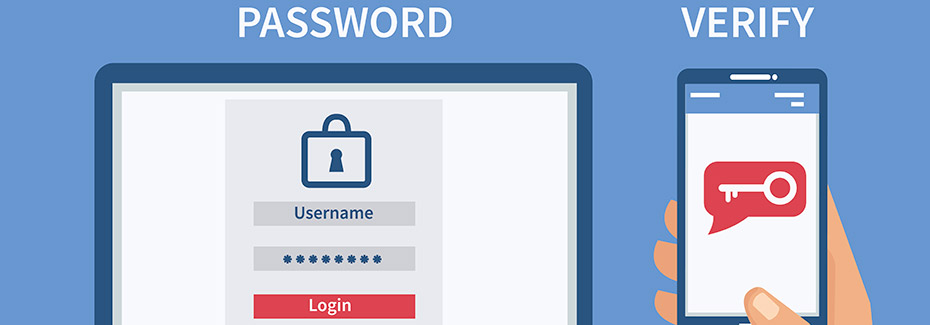
Here’s an example of what multi-factor authentication (MFA) is not. For instance, you head to your online bank account to login. Entering the username and password into the designated fields and click on login. From here, you’ve gained access to your bank information. Easy peasy and you go about your business. Wait one second! If you’re one of the 54% of consumers who use five or fewer passwords for all of your online accounts, you could be setting yourself up for failure.
Recycling passwords is a big no-no. We highly advise coming up with unique passwords for all digital channels. We published a blog post discussing the importance of unique passwords and why using the same password is bad.
Let’s dive right in and discuss the benefits of multi-factor authentication.
What Exactly Is MFA?
Multi-factor authentication, sometimes referred to as two-factor authentication (2FA), is defined as a security enhancement that allows you to present two pieces of evidence when logging in to an account. An example of multi-factor authentication is using your debit card to purchase an item. The first step is inserting your card for payment. The second step is entering your personal ID number (PIN). Lastly, accepting the terms of the payment on the payment pad. The real-world transaction is complete.
To demonstrate a digital transaction – let’s use email. The traditional method of logging into your email account is typing in your email address and password. Click on the submit button and you’re off to your inbox. Notably there’s no additional authentication that takes place between the login process.
Of course the example provided is a common case lots of individuals experience when accessing their email. However, what about adding multi-factor authentication? Although the process is virtually the same, there’s one small caveat added. A second verification step. For example the step can consist of receiving a text message, using an authentication app, or using a fingerprint on a device. As long as there’s a middle step added that is unique to you, this is considered multi-factor authentication.
To summarize, implementing multi-factor authentication is a step in the right direction for any business. Safeguarding all of your email, data, and other valuable digital assets is a cybersecurity measure all businesses cannot afford to disregard in today’s digital world.
How Can Small Businesses Benefit From MFA?
For starters, implementing MFA helps protect you with an additional layer of security. The extra layer makes the task of accessing data more difficult for the bad guys. In other words, if an uninvited hacker was attempting to log into your bank account and MFA was implemented – the individual will not be able to get past the middle step. A text message to the owner of the email account. Unless the hacker has access to the individual’s mobile device, chances are low the hacker can gain access to the account.
Implementing MFA for your business is a smart move. If you partner with a Managed IT Service provider these technical experts can guide you in deploying MFA for specific applications. You should use MFA whenever possible, especially when it comes to the company’s sensitive data. Email is a an application business’ should flip the MFA switch to on.
To point out email is an easy example. However, we know dealing with an extra security layer is annoying. The task of entering a code or personal ID number is cumbersome. We get it. Although if an email account were to get hacked and didn’t have MFA implemented – would you mind an extra 2-3 seconds of your time to secure your account? Even worse, if a CEO’s email were to get hacked and used for email phishing purposes. Imagine a CEO emailing employees or customers asking for wire transfers, gift cards, or other out the ordinary requests? Chances are high the recipient will perform the task. A phisher has become aware of who’s susceptible to these requests.
As business’ continue to strive for stronger cybersecurity techniques we highly recommend implementing MFA at the minimum. See how Zuma Technology can help turn on MFA for your business today!

I agree that two factor authentication increases security, but I would also say there is a sliding scale regarding how secure each method is. For example, if you receive a one-time password via an SMS message (rather than from an app or hardware token) you will be open to sim-swap attacks. Apps on your phone are prone to viruses and rogue apps, and hardware tokens are attacked either at the server side, or via phishing attacks (another alternative would be to use a Fido key, but these usually require plugging in to a USB Port which itself may violate company security policies).
All solutions have their pros and cons but 2fa is clearly more secure than relying on a username and password alond.
Hello Jeff –
We definitely agree, there’s pros and cons to all security protocols. Managing IT for businesses continues to evolve at break neck speed and implementing small but might protocols like MFA is a good start. We are advocates for increasing security as much as possible and we feel it’s our responsibility to educate the community on best cybersecurity practices. Thank you Jeff for the insight! Always fun chatting with a fellow cybersecurity individual.